Rising scope for self-sufficiency in rice production
BRUNEI Darussalam could soon achieve self-sufficiency in rice production if the country takes a bold initiative in implementing commercial paddy projects based on the findings of a recent study which found many areas in the country suitable for paddy cultivation.
According to the latest figures made available in 2014, the Sultnate’s rice production meets only four per cent of the total demand, falling way behind the government’s target of 60 per cent for 2015 set in 2009.
The main objective of the Detailed Environmental Impact Assessment (DEIA) study was to assess the impact of commercial paddy cultivation on the environment and formulate management strategies to ensure sustainable production.
According to the findings of the study conducted by a consultant agency Technotest Sdn Bhd, majority of the project areas currently used for paddy cultivation and new areas proposed for development, were found suitable for commercial production without environmental impacts, and will significantly contribute to the nation’s rice production.
The areas under assessment were Wasan, Junjongan, Batong, Batang Perhentian, Bebuloh and Panchor Murai in Brunei-Muara District and Selapon, Lekiun-Perdayan, Senukoh and Sipal in Temburong District.
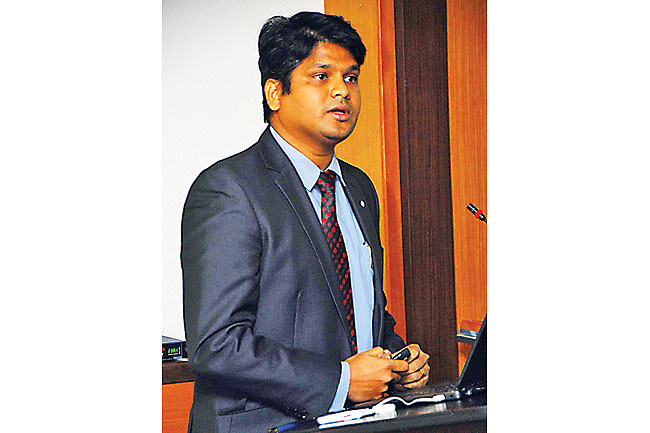

Dr Biswajeet Pradhan, Project Team Member and Associate Professor of Universiti Putra Malaysia during the presentation. – COURTESY OF DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE AND AGRIFOOD
Of these, Wasan, Junjongan, Panchor Murai, Batang, part of Batang Perhentian, Selapon and Sipal areas were found suitable for implementing commercial paddy production projects.
However, parts of Batang Perhentian, Lekiun-Perdayan and Senukoh were found unsuitable as further expansion and mechanised cultivation of the areas would have significant adverse environmental impacts due to the presence of deep peat soil, the report said. As such, it is more appropriate to conserve these peat soil areas as it has many ecological benefits including conserving bio-diversity, as a source of renewable bio-resources. These areas can help in mitigating floods and greenhouse gas emissions as well as store carbon besides being part of the country’s natural history, the report added.
The report revealed that the assessed project areas are free from nitrate and pesticide contamination because the current usage of fertilisers and pesticides for paddy cultivation is still within safe limits.
Appropriate mitigation measures also have been suggested in the report to prevent or minimise the impact to the environment, among them include identification and conservation of endangered species of flora and fauna, reducing use of pesticides through integrated pest management and giving training to farmers/farm workers on health safety measures while handling pesticides.
The DEIA study report has proposed formulation and implementation of an Environmental Management Plan (EMP) which should include plans to monitor the impact not just on the environment but also public health, providing a health emergency response, rehabilitation and abandonment plan.
It also recommended the formulation and enforcement of regulations to restrict the use of peat soil for paddy cultivation and other crop production activities from an environmental perspective, besides emphasising the need to develop mechanisms to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions from paddy cultivation and supporting sustainable development in line with the recommendations of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) held in Paris in December last year.
To ensure continuity in the implementation of commercial paddy production projects in the country to gain knowledge in addressing environmental issues, six officers from the Department of Agriculture and AgriFood recently conducted a study tour to Malaysia. The team visited Vi Chem – an accredited laboratory analysing environmental samples, Universiti Putra Malaysia, the Department of Environment, Malaysia and the paddy cultivation project in Tanjong Karang.
The report presentation was held at the Department of Agriculture and AgriFood Headquarters in Berakas. The event was attended by Hajah Khartini binti Haji Musa, Acting Deputy Director of Agriculture and AgriFood, senior officers and staff of the Department of Agriculture and AgriFood. On behalf of Technotest Sdn Bhd, Dr Biswajeet Pradhan, Project Team Member (Environmental and GIS Specialist) and Associate Professor of Universiti Putra Malaysia presented the findings of the projects.
Tarikh Input: |
Kemaskini: 11/07/2019 | amirahsyahira
PERKONGSIAN MEDIA